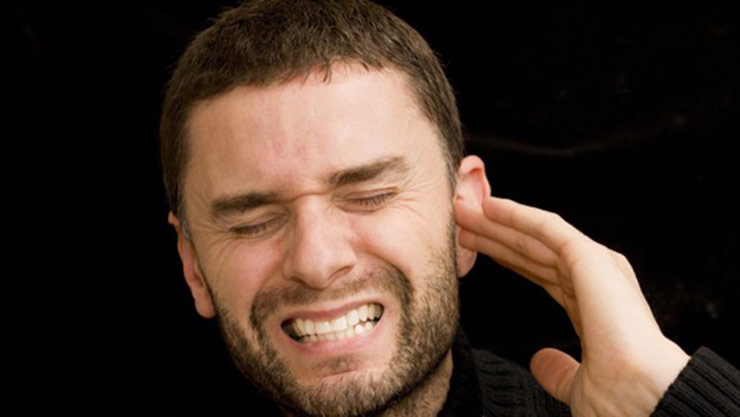

Tinnitus
Tinnitus or ringing in the ears is a common problem that affects about 15 to 20 percent of the people. It is usually a symptom of another underlying condition like muscle dysfunction, wax build-up, ear injury or a circulatory disorder.
If you suffer from Tinnitus this simple little trick may help give you some relief.
Dr. Jan Strydom, of A2Z of Health, Beauty and Fintess.org. instructs:
“Place the palms of your hands over your ears with fingers resting gently on the back of your head. Your middle fingers should point toward one another just above the base of your skull. Place your index fingers on top of you middle fingers and snap them (the index fingers) onto the skull making a loud, drumming noise. Repeat 40-50 times. Some people experience immediate relief with this method. Repeat several times a day for as long as necessary to reduce tinnitus.”
The most likely reason that this technique works is because you are causing the suboccipital muscles to relax and reduce tension. A common cause of Tinnitus is due to tight, painful suboccipitals. The suboccipital muscles are always on as they are constantly working to with the other muscles of your neck to keep balanced on top of your spine. In particular they initiate and control fine movements. Lately these muscles are getting taxed more and more as people spend additional time in front of a computer at work, or stretching their neck forward to look at their tablet tablet or phone. Muscles that are always contracted are tight and painful. Muscles that are overstretched are long and weak. The suboccipital muscles are a source of pain for a lot of people who have tinnitus and are a common cause of “tension” type headaches.
Tapping a muscle belly or tendon quickly is a good way to cause a muscle to contract. When you go to the doctor and they test your muscles this is happening. Continual tapping or constant pressure provides the opposite effect: they overload the muscle, causing it to burn up all of it’s electrolytes and ATP and other resources it needs to activate and contract on a regular basis. When muscle cells become energy depleted, they turn off and once enough cells turn off, the muscle as a whole relaxes and you feel instant pain relief.
That said, maybe this trick can at least offer you some brief relief. Perhaps right before you try to go to sleep at night. Keep in mind that it doesn’t work for everyone. Give it a shot and see what happens.





 © 2025 - NATIONAL DENTAL SYSTEMS, INC. | 430 NORTH MAIN ST. SALEM, UT 84653 | CALL US TOLL-FREE 855-770-4002
© 2025 - NATIONAL DENTAL SYSTEMS, INC. | 430 NORTH MAIN ST. SALEM, UT 84653 | CALL US TOLL-FREE 855-770-4002